- News
Shanghai General Hospital Digestive Department Successfully Applies EUS-NOTES Techniques to Treat a Complex Case of Advanced Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma with Acute Obstructive Suppurative Cholecystitis
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/8Hg6dEABgaGH21grzUmZKA
An elderly patient diagnosed with advanced hilar cholangiocarcinoma complicated by high-level obstructive cholangitis and acute obstructive suppurative cholecystitis faced a life-threatening challenge: how to quickly control the infection and prevent septic shock in the absence of surgical options.
Faced with this dilemma, the Digestive Department (South Campus) at Shanghai General Hospital, led by Associate Director and Endoscopy Center (South Campus) Director Prof. Baiwen Li, employed a combination of minimally invasive endoscopic techniques. These included endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), EUS-guided biliary Profainage (EUS-BD), and EUS-guided gallbladder Profainage (EUS-GBD), collectively part of the natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) approach. This innovative treatment successfully resolved the patient’s biliary obstruction and obstructive cholecystitis. The patient recovered well and was recently discharged.
The 82-year-old patient, Ms. Zhong, presented with persistent upper right abdominal pain, jaundice, and high fever, which progressively worsened. Her family rushed her to Shanghai General Hospital’s Songjiang campus, where Prof. Li’s team conducted a comprehensive evaluation. Ms. Zhong was diagnosed with Type IV hilar cholangiocarcinoma with high-level obstruction and regional lymph node metastasis. Given her advanced cancer and advanced age, surgical intervention was not an option. The team prioritized bile Profainage to alleviate jaundice and infection control to stabilize her condition. Following a multidisciplinary team (MDT) discussion and thorough communication with the patient’s family, the experts decided on a minimally invasive endoscopic approach.
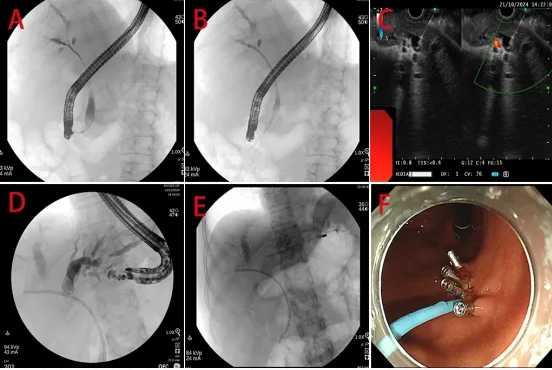
On the day of the procedure, Prof. Li’s team initially attempted bile duct Profainage using traditional ERCP. However, they encountered severe obstruction at the hilar region. After repeated efforts, a stent was successfully placed in the right intrahepatic bile duct, achieving right liver Profainage. Unfortunately, attempts to access the completely blocked left intrahepatic bile duct failed.
The team then decisively switched to EUS-BD. Using real-time EUS guidance, the left intrahepatic bile duct was successfully Profained, significantly improving the patient’s symptoms, with rapid reductions in liver enzymes and bilirubin levels.
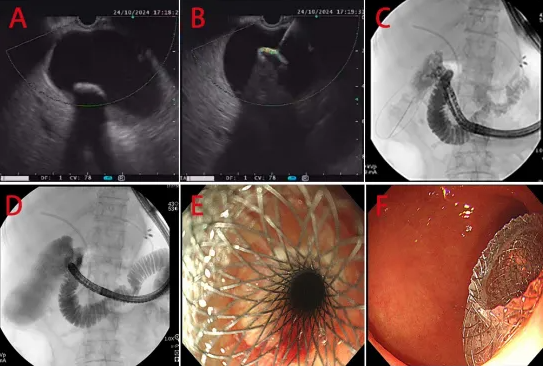
The day after the first procedure, the patient developed a high fever and right upper abdominal pain. The team identified acute obstructive suppurative cholecystitis caused by tumor-induced cystic duct obstruction, posing a severe infection risk. While percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder Profainage (PTCD) is a standard option, it carries risks of complications such as skin fistulas and infections. Considering the patient’s advanced cancer, the team opted for EUS-GBD after discussing the plan with her family.
Under EUS guidance, Prof. Li precisely punctured the gallbladder, avoiding vascular structures. A lumen-apposing metal stent (LAMS) was placed between the duodenal bulb and the gallbladder. The procedure immediately Profained a large volume of purulent bile, which was flushed until clear. Remarkably, the operation was completed in just 15 minutes. The patient’s abdominal pain was relieved, her fever normalized within a day, and she resumed eating two days post-procedure.
In recent years, therapeutic EUS has rapidly evolved, particularly in NOTES procedures, which overcome the limitations of traditional endoscopy. The Huating Endoscopy Team at Shanghai General Hospital’s South Campus is among the first in China to adopt EUS-NOTES techniques. The team has performed numerous procedures, conducted related clinical research, and developed specialized instruments, continuously refining this cutting-edge approach.
This case marks the first-ever documented use of combined ERCP, EUS-BD, and EUS-GBD to treat a complex case of advanced hilar cholangiocarcinoma with high-level obstructive cholangitis and acute obstructive suppurative cholecystitis. A literature review revealed no prior reports of such a combination, highlighting the pioneering nature of this achievement.
Reporter: Prof. Baiwen Li, Digestive Department (South Campus)
Editor: Public Relations and Spiritual Civilization Office, Shishi Cai
Translator: International Cooperation and Exchange Department, Yuhan Wang
