- News
Robotic Surgery Brought "New" Life to the Bladder
Link of the original article:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/OuDxO3sGZoMBEx9-k0ILjg
Bladder cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors of the urinary system. When the disease progresses to high-grade muscle invasive bladder cancer, patients often need radical cystectomy.
Although radical cystectomy is an important approach in the treatment of bladder cancer. However, with cystectomy and urinary diversion, the quality of life of patients decreases to varying degrees, which is also the main reason for most of patients to accept radical cystectomy.
Radical cystectomy has undergone evolution over the years. With the application of Da Vinci robotic surgery system and the continuous improvement of surgical approaches, orthotopic neobladder surgery has been widely applied. From the principle of surgery, it also represents our pursuit for a better quality of life in terms of the principle of surgery .
Radical cystectomy and urethral diversion
After cystectomy, the ureter needs to be anastomosed. The common anastomoses are ureterostomy, ileal catheter Bricker bladder and orthotopic neobladder.
Ureterostomy:
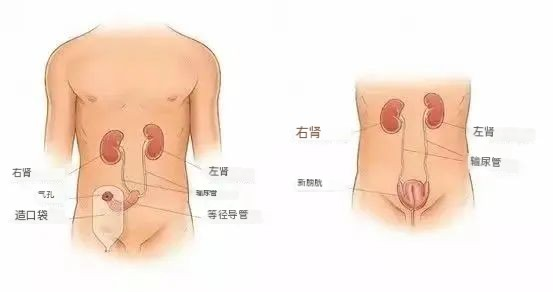
As the name implies, the ureteral end is directly anastomosed to the abdominal wall, and urine is collected through a pocket. This surgery is simple, but it requires long-term replacement of the ureteral stent after that, and there are many complications, such as infection, retraction, urinary fistula, stricture and so on.
Ileal conduitileal-Bricker bladder:
The ileal catheter-Bricker bladder is performed by using a section of about 250px ileum as the transitional segment, anastomthe ureter to the ileum, then to the abdominal wall and collecting urine through the ostomy pocket. By using the ileum as a transition catheter, a series of postoperative complications such as ureteral stenosis, hydronephrosis, and infection are greatly reduced,, and the stent tube is no longer needed to drain urine. However, patients still need to wear plastic bags to collect urine.
Orthotopic neobladder:
It is to rebuild a "new bladder" in the position of the original bladder. Usually, a segment of ileum will be amputated and "made" into a bladder, which will be sutured with the ureter. It can restore to the preoperative physiological state to the greatest extent, and obtain urination and urinary control functions similar to those of normal people, which not only guarantees the beauty, but also helps patients return to normal life.
Orthotopic bladder construction under complete robot:
In recent years, the technology of in situ bladder construction in vitro has become mature, but due to the problems of large incision, various surgical procedures, complex technology and long operation time, it is only applied in a few large medical centers. Moreover, due to the problems of more perioperative complications and longer postoperative recovery time of patients, many patients and doctors are discouraged and cannot be carried out as a conventional technology.
The urology center of Shanghai General Hospital has installed the first fourth generation Da Vinci Xi robotic surgery system in Shanghai since 2019. At present, more than 1000 robot assisted laparoscopic surgeries have been completed, including radical cystectomy, partial nephrectomy, radical resection of huge renal cancer, radical resection of huge adrenal tumor, radical resection of prostate cancer, hemiurinary tract resection, pyeloplasty and other level IV operations, The surgery effect was recognized, and the patient recovered satisfactorily.
After the establishment of the second Department of urinary oncology in the clinical medical center of urology in May 2023, under the leadership and support of Professor Shujie Xia, the leader of the center, Professor bangmin Han, the director of the center, and Professor Liu Cheng, the director of the second department of urology, Professor Hai Bi, deputy director of the department, innovatively carried out orthotopic bladder construction under complete robot, which fully reflects the rapid recovery advantages brought by minimally invasive technology. In this case, intestinal recovery, postoperative pain and wound problems can be solved, and complete robotic orthotopic bladder has brought great benefits to patients.
The advantages of orthotopic neobladder surgery are very obvious. It can urinate from the urethra as usual, and does not need to stick a urine bag on the abdominal wall. However, the surgery is not suitable for all patients. Before the surgery, the surgeon will conduct a comprehensive evaluation for the patient to make sure he is in good condition, the tumor is in the bladder neck and urethra, the intestinal condition is good, and the requirements of a neobladder can be met.
Since the establishment of the second department of urological oncology, 8 cases of radical cystectomy have been completed in two months, including 3 cases of fully robotic orthotopic bladder construction.
Introduction of the second Department of urological oncology
In 2023, in order to further improve the level of discipline development in the diagnosis and treatment of urological tumor, Shanghai General Hospital brought in two well-known experts Professor Liu Cheng and Professor Bi Hai from the Third Hospital of Peking University, and selected elite surgeons to establish the department.

Adhering to the concept of "providing world-class care for every patient", the department integrates the medical advantages of urology in Beijing and Shanghai, adopts the advanced diagnosis and treatment technologies and concepts at home and abroad, and specializes in the latest generation of Da Vinci robotic system to implement difficult minimally invasive surgery. Special emphasis is placed on the diagnosis and treatment norms while paying attention to the individualized treatment according to the specific conditions of different patients and the comprehensive application of the latest treatment plans at home and abroad. The discipline leaders of the department have high popularity and influence in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer, bladder cancer, complex renal cancer and cancer thrombus in China.
Members of the department presided over 8 national research projects and published more than 60 academic papers at home and abroad, including JNCI, genome biology, int J Surg and other international academic journals. The team has a lot of fruitful cooperation with internationally renowned medical institutions such as Karolinska Medical College in Sweden and San Antonio Medical Center in the United States, and has established joint research centers with national top research institutions such as the State Key Laboratory of biochemical engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, laying a solid foundation for the innovation and transformation of medical engineering cooperation.
Main clinical features: diagnosis of prostate cancer, bladder cancer, kidney cancer and other urinary system tumors, robot minimally invasive surgery treatment and whole process comprehensive and precise treatment; Robot radical prostatectomy with preserved sexual function and urinary control function, complete endoscopic total cystectomy and orthotopic bladder reconstruction, precise treatment of advanced bladder tumor, radical surgery and whole course management of renal cancer with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus, complex kidney preserving machine human assisted renal tumor resection and minimally invasive radical nephrectomy, minimally invasive surgery and whole course comprehensive treatment of renal pelvis and ureter cancer.
