- News
The Department of Orthopedics at Shanghai General Hospital Completed First Full Spinal Endoscopy with Spine-specific Laser Treatment
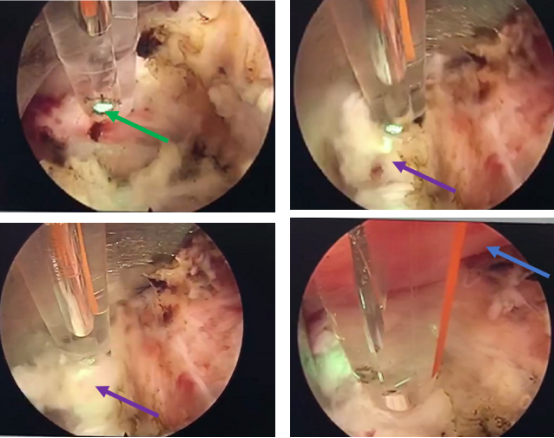
Recently, Dr. Fu Qiang, director of the Department of Spine II (North) of the Orthopaedic Clinical Medicine Center, treated a patient with a huge lumbar disc herniation using full spine endoscopy combined with a special spine laser. The patient had undergone five surgeries for a malignant bone tumor, resulting in severe adhesion in the lumbar spinal canal. Through a 5 mm incision, a laser fiber was used to excite the spine-specific laser to separate, ablate, and vaporize the adhesions around the nerve of the herniated disc, and the prolapsed disc was then successfully removed. The surgery bled only 5 ml and took only 23 minutes to complete. This was the first spinal endoscopy combined with laser surgery completed in the spine surgery department of Shanghai General Hospital.
The patient,36 years old, had undergone 5 repeated surgeries for malignant bone tumors in both lower extremities, and weighed more than 200 pounds under the side effects of long-term postoperative chemotherapy and hormone therapy. Two weeks ago, the patient suddenly developed radiating pain and numbness in the right lower extremity, which radiated to the right plantar aspect of the foot, making it impossible for her to walk.
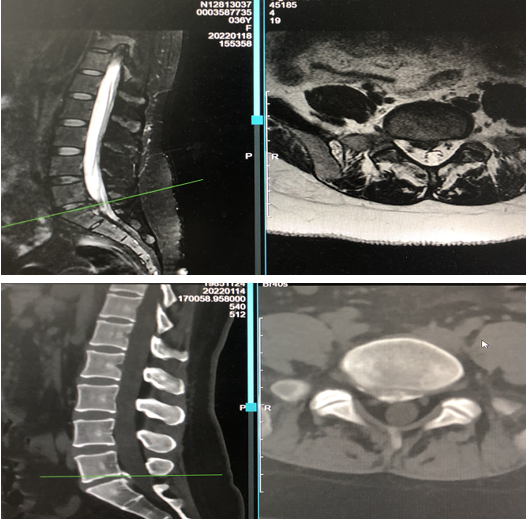
Luckily, she was diagnosed by the team of Dr. Fu Qiang. On admission, the patient was found to have a fibrosarcoma with possible systemic metastasis, poor condition, a large disc prolapse between L5-S1 of his lumbar spine combined with significant calcification, and severe neural adhesions in the lumbar spinal canal.
The surgical team discussed that conventional open lumbar fusion surgery is a major operation. If an open lumbar fusion approach is implemented, the process of forcibly removing the disc and separating the adherent tissues will greatly increase the risk of intraoperative nerve injury and postoperative infection may occur. After careful evaluation and communication with the patient and her family, the expert team decided to treat her with a full spinal endoscopy combined with dedicated laser surgery through the intervertebral plate.
Through a 5 mm incision, the surgical team precisely punctured the herniated disc, established a working channel and inserted the spinal endoscope. Under a 50x magnified view, the team found severe adhesions around the nerve tissue in the lumbar spinal canal and a large prolapsed disc ventral to the nerve root with calcification. They placed a pre-connected laser fiber through the working channel to excite the spine-specific laser and safely and effectively removed the adhesions around the herniated disc nerve using laser separation, ablation and vaporization functions. The surgery took only 23 minutes, with only 5 ml of intraoperative bleeding.
According to experts, one of the difficulties of spinal endoscopic surgery is intraoperative hemostasis. The surgical bleeding can cause visual field obstruction and increase the operating time and surgical risk. The traditional radiofrequency method needs to be applied closely to the tissue during surgery, which makes the local tissue temperature rise to 60°C to cause protein denaturation and achieve hemostasis. However, due to the slow conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy, the local temperature of the tissue rises slowly and the hemostasis efficiency is low. The high energy of the spinal laser converts light energy into heat energy faster, and the energy can be absorbed quickly by the tissues and reach the hemostatic temperature, which is complemented by endoscopic technology, with the advantages of smaller wounds, less bleeding, and faster postoperative recovery. Previous experimental studies and clinical experience have shown that laser surgery have less postoperative back pain and lower postoperative inflammatory response of the disc. The surgery not only demonstrated the excellent diagnosis and treatment level of the second spine team, but also reflected the concept of patient-centered, personalized and precise medical services.
(Correspondent:Guo Song, Orthopaedic Department, Zhang Jingyu, Medical Affairs Department)
