- News
Scientific Research | Nature Communications Published the New Research Progress on Gastric Cancer Treatment Made by Professor Chen Huang and Professor Guangjian Fan’s Team
Source: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/WISF81zMPBVv9ei0dj_z2w
Recently, Nature Communication published an article written by the research team of Professor Chen Huang and Professor Guangjian Fan, the title of which is “Lactylation of METTL16 promotes cuproptosis via m6A-modification on FDX1 mRNA in gastric cancer”. The article elaborated the driving role of METTL16 in cuproptosis, reflected the importance of lactylation and m6A-modification in gastric cancer progression, and provided new directions and ideas for targeted therapy of gastric cancer. Both Professor Chen Huang and Professor Guangjian Fan are the corresponding authors. Doctor Lianhui Sun, Yuan Zhang, Boyu Yang and Sijun Sun of our institute are joint first authors.

Gastric cancer is a common malignant tumor in digestive system. Existing studies have shown that exploring key protein lactylation modifications in the progression of gastric cancer and their specific action mechanisms are of great importance to find out new clinical diagnostic and treatment options for gastric cancer. Professor Huang and Fan’s research team found that copper ions gathers at the gastric cancer focus; the concentration of copper ions exists a positive correlation with the progression of gastric cancer and a negative correlation with patient prognosis.
After the proteomics screening and functional validation, it is identified that methyltransferase METTL16, which is an atypical methyltransferase, is a key controlling molecule in the process of cuproptosis. Previous studies have shown that METTL16 can regulate the development of various human diseases through m6A modification, which is a common form of epigenetic modification. And the research team found that lactic acid can lead to METTL16-K229 lactoylation, which further improves m6A modification of FDX1 mRNA, increases FDX1 mRNA expression, and ultimately leads to the cuproptosis of gastric cancer cells.
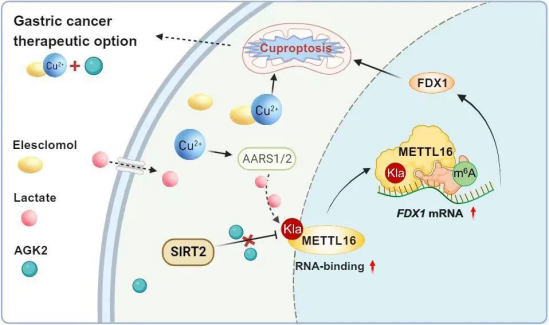
It is also found in the research that mechanistically, it is the copper ions that promote the overall m6A modification in gastric cancer, and the METTL16-mediated FDX1 mRNA - m6A plays a crucial role in accelerating the cuproptosis. Specifically, copper ions modulated the activity of METTL16-K229 lactoylation by regulating both the lactonase SIRT2 and delactonase SIRT2. Lactoylated METTL16 causes methylation modification at the FDX1-602 site, which promotes FDX1 expression and ultimately leads to the cuproptosis. During this process, AGK2, the inhibitor of SIRT2, significantly accelerates the lactoylation of METTL16 and promotes m6A modification of FDX1, speeding up the cuproptosis. Therefore, combining AGK2 with cuproptosis inducer, irisimab (Eles), could facilitate the treatment of malignant gastric cancer.
Moreover, it is worth mentioning that this study also found that copper ions reach to higher levels in gastric mucus-secreting adenocarcinomas and correlated more significantly with tumor vascular invasion, which is a sub-type of gastric cancer, and utilizing cuproptosis in the treatment of this sub-type seems to be a promising therapeutic strategy that deserves further study.
